
Research
How is the homeostasis of hematopoietic stem cells (HSC) regulated at the molecular level?
The long-term goal of the Zhao lab is to understand basic regulatory mechanisms of general and malignant hematopoiesis from the perspective of gene regulation, especially at the post-transcriptional level.
The Zhao lab is also interested in exploring regulatory mechanisms of the activation and inhibition of ferroptosis under the context of hematopoiesis and leukemogenesis.
Questions & Approaches
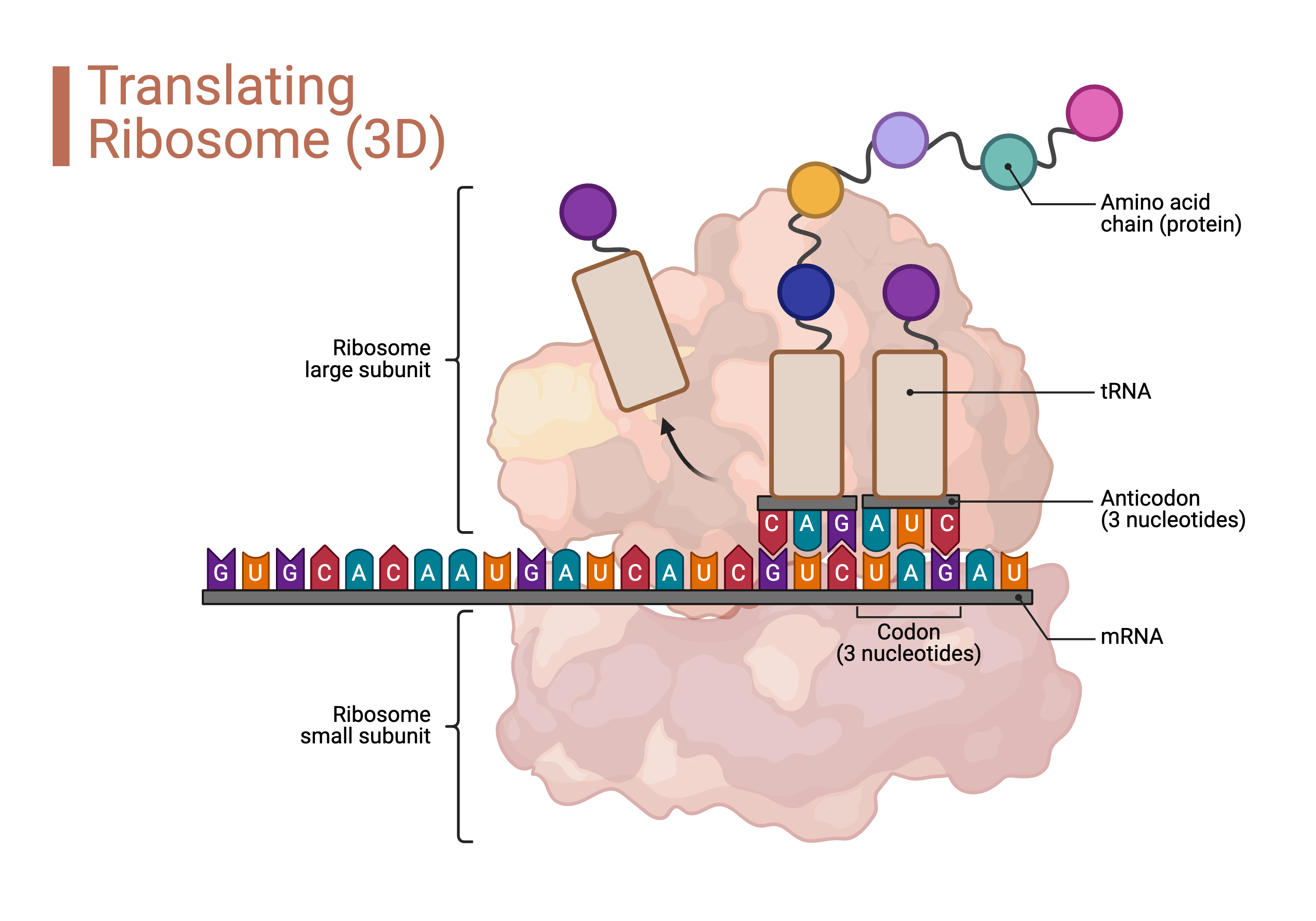
Regulations of HSC functions at the post-transcriptional level
Impaired HSC function can result in virtually all kinds of hematologic disorders, including non-malignant and malignant diseases (i.e. leukemia). One unique characteristic HSCs possess is the highly regulated protein synthesis rate. Higher or lower protein synthesis can both impair HSC functions. Therefore, the Zhao lab aims to understand how protein synthesis rate determines the HSC functionality and how HSCs maintain such a precisely regulated protein synthesis rate.
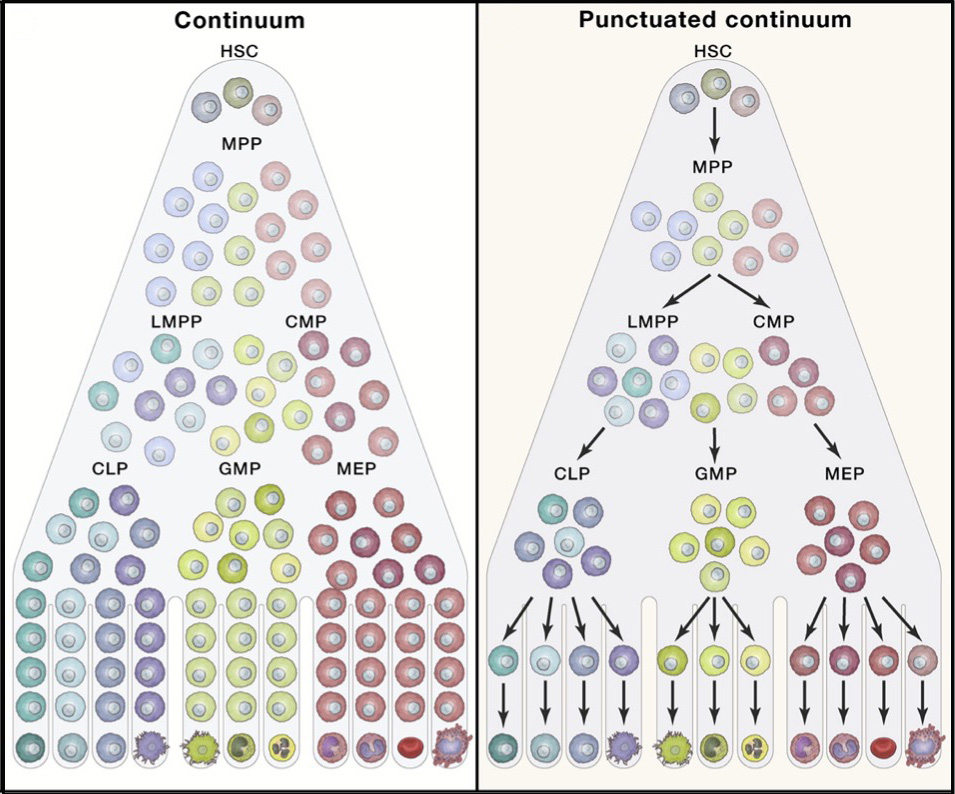
Cell fate decision of HSC & leukemogenesis
The Zhao lab is also interested in understanding how normal hematopoiesis transforms to malignant. Dr. Zhao aims to understand how blood cell differentiation occurs from the perspective of post-transcriptional gene regulation, and what genetic perturbation occurs when normal hematopoiesis is dysregulated and transforms to malignant hematopoiesis.
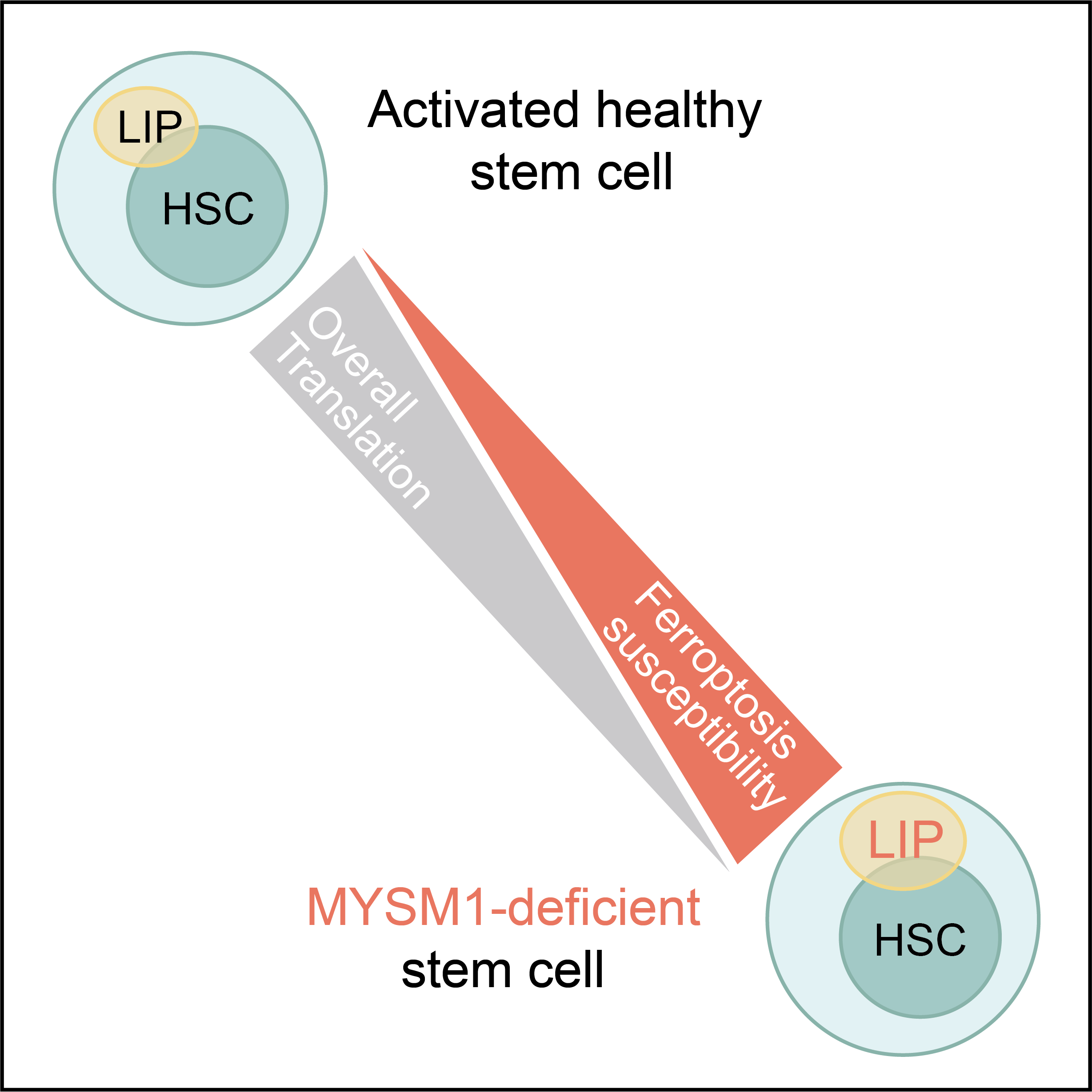
Mechanisms in ferroptosis
To use ferroptosis as a legitimate therapy for cancer patients, its potential adverse effect on hematopoietic stem cells has to be resolved. Therefore, a detailed mechanism by which how ferroptosis occurs and is regulated in normal cells, especially in stem cells, has to be fully understood. Based on this finding, Dr. Zhao aims to use human hematopoietic stem cells, as well as other normal cells as models to study detailed mechanisms by which ferroptosis is induced or inhibited.
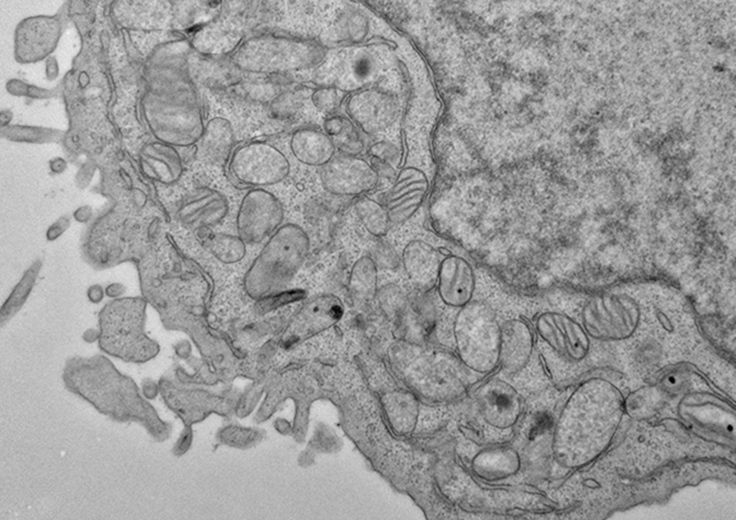
Heterogeneity in sensitivity to ferroptosis induction
Ferroptosis is a unique type of cell death related to imbalanced redox active ferrous iron in the cell. However, some cells are exceptionally refractory to ferroptosis induction, while others are extremely sensitive. The heterogeneity of ferroptosis sensitivity appears to be attributable to intrinsic heterogeneity of different cell types. Therefore, the Zhao lab aims to understand the detailed mechanisms that determine the heterogeneity of the sensitivity of ferroptosis in different cell types.